Using Semalt's Webpage Analyzer To Understand Important Elements For Page Ranking
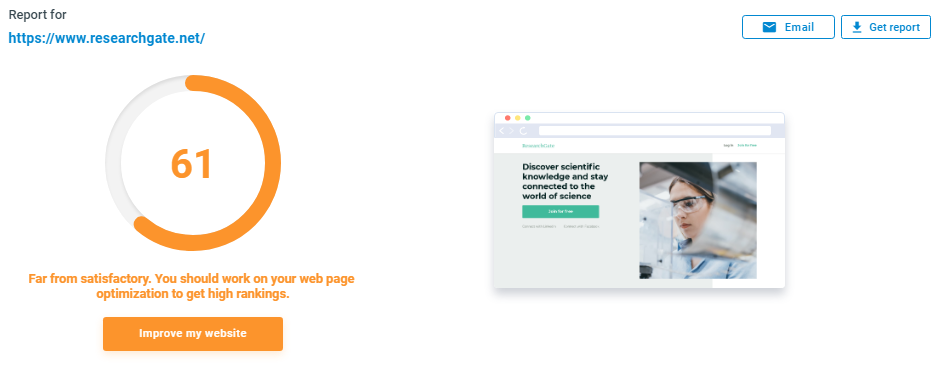
If your goal is the growth of your website, this practice starts with a site audit. The most effective audits come from using a website analyzer to understand where your website needs to improve. You can do this by utilizing Semalt's webpage analyzer.
We will be going through the 54 points of importance you need to consider for complete website analysis. By the end of this article, you will have some tips and tricks that you can use to improve your website's searchability.
Website Analyzer Section One: Search Engine Optimization
A website with the right SEO is easy for Google to locate. Semalt's analysis tool covers a wide variety of Google's needs from on-page optimization. That means that the target page is the primary focus, not all of the directories and subdomains beneath the page.
You can feasibly take an analysis of each page individually to find out specific errors. In the SEO section, Semalt prioritizes the following areas:
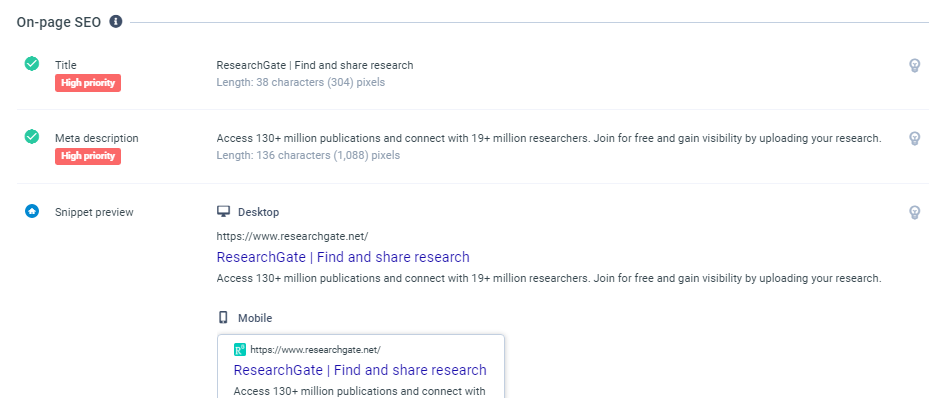
Page Title
The page title is what first appears on a SERP. It is the largest text that is located within a <title> HTML tag. It typically contains the name of the website but may contain what the website does. By placing some target keywords from your niche here, you may improve your SEO.
Meta Description
A meta description is located just below the title on the SERP. It is typically around 130 characters and contains additional keywords detailing the page. These are incredibly important and often forgotten on websites.
Snippet Preview
The snippet preview appears on the SERP and contains the URL, title, and meta description in order. Character limitations are essential here, as it is vital to use these limitations to fill your snippet with useful information that informs the searcher of what your site offers.
Headings
If you have ever seen a tag with the letter H followed by a number (H1, H2, etc.), these are known as headings. An H1 tag is typically the second most crucial part of ranking for search. By planting specific keywords here, you have the potential to rank for your target niche.
In-Page Links
In-Page links are a combination of internal and external links on the page. Typically, these links should be to navigational elements, social media pages, and your website's goods and services. Anchor text informs the follower of where these links may go.
Text / HTML Ratio
The text to HTML ratio measures the amount of code vs. the amount of text on your website. All pages typically have more code than text, given the amount of effort it takes to build the visual and functional elements. Try and keep your code lightweight to increase page loading speed, which is a factor in determining your SEO.
Image ALT Attribute
ALT attributes on images inform the user of the contents of the photos. It acts as a potential SEO improvement factor and makes your website accessible to those who would not see the images usually (i.e., the blind). They are often forgotten and have the potential to include important keywords.
Most Common Words
The "most common words" section includes three critical areas:
- Most common words
- Most common two-word-phrases
- The most common three-word-phrases
This area is essential when determining the amount of keyword consistency between locations. Repeating a keyword in multiple sections is one way to inform Google of the details of your website. Semalt recommends placing them in your title, meta description, headings, alt tag, and body content whenever possible.
With natural keyword density, Google will see this as a confirmation of the theme of your content. Do not try and force a three-word-phrase into a section where it won't make sense. Google's AI can pick up on this, so avoid keyword stuffing at all costs.
Words Per Page
Businesses hate body copy, but those who do not have a minimum description of 300 words won't have enough detail on their website. Semalt sets this as a reasonably high priority, understanding the importance of providing just enough information to describe your page.
Content Uniqueness Check
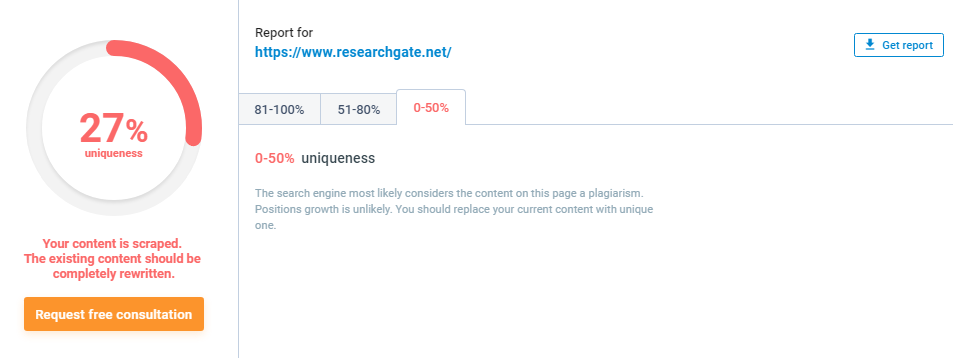
While having similar target keywords to your competitors is essential, Google needs to recognize the importance of seeing your page as a unique entity. If your site looks eerily similar to others, your content may need rewriting to address uniqueness.
Section Two: Indexing
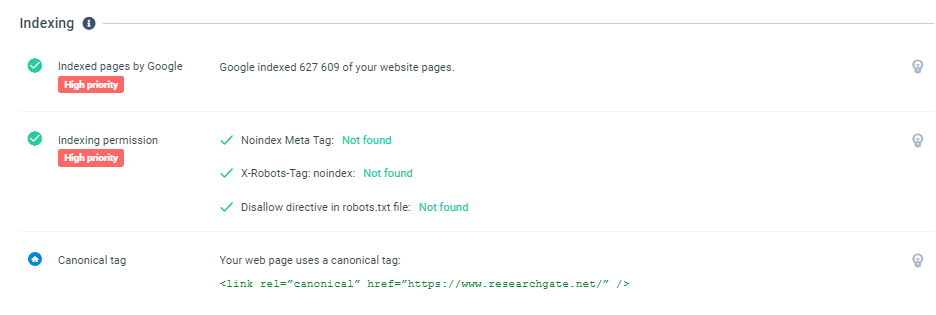
Indexing is the process of listing your website on the search engine. To be indexed appropriately, Google needs to be able to individually crawl (or navigate) through each of your pages. Google does this through navigational links, which are typically on the top of your website.
Here are the sections that the website Analyzer has associated with Indexing:
Indexed Pages By Google
This section tells you the number of pages that Google can index. If the search engine cannot navigate your website, they may not list them all. This navigation is essential, as websites rarely rank for the main page, especially when starting.
Typically, sites address this issue by having multiple blog posts to flush out page number, meta descriptions, and content which contains keywords important to their business. You also need to provide indexing permission.
XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is an expanded directory of your website specifically for Google's AI. Google reads the sitemap and uses that information to find which pages you prioritize as most important. It also speeds up the search process by providing a roadmap for Google, allowing them to know the preferred route.
Custom 404 Page
A custom 404 page is necessary when trying to prevent people from leaving your site, regardless of an error occurring. The error will redirect them to another section of your site. Keeping them on your site allows them to stay on your site. By extension, this reduces your site's bounce rate.
Underscores in Links
Google's engine recognizes underscores as nonexistent. As a result, putting an underscore in your URL will mash the two pieces of text together. To address this issue, Semalt recommends that you place hyphens instead.
Section Three and Four: Analytics, Counters, and Structured Data
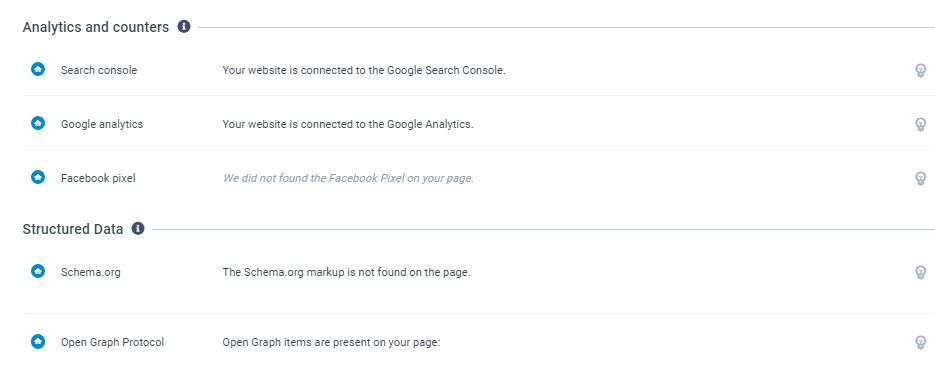
Starting with the analytics and counters section, it checks to see that you have a connection to three separate analytics platforms:
- Google Search Console
- Google Analytics
- Facebook Pixel Helper
The first two are for tracking the effectiveness of Google search and ads. Google Analytics is beneficial in providing data that supplements Semalt's systems. The third bullet is Facebook's version of Google Ads, which tracks information related to advertising campaigns you start on Facebook.
The last three sections require a bit more detail:
Schema.org
Schema.org is a markup code developed by Google. Websites that use this structured data platform can create a rich snippet that displays their page content uniquely. For example, recipes require a specific schema code.
Open Graph Protocol
The open graph protocol creates unique stages for each web page that seek to enhance the metadata. This protocol is typically for sorting different sections of a website. They are less common for sites with unique photo situations (Instagram, Twitter, Facebook, etc.).
Microformats
Microformats modify your HTML to create and send information related to events, business cards, and product reviews. They integrate with software like Microsoft Outlook, Google Maps, and Thunderbird to send this information.
Section Five: Mobile Adaptability
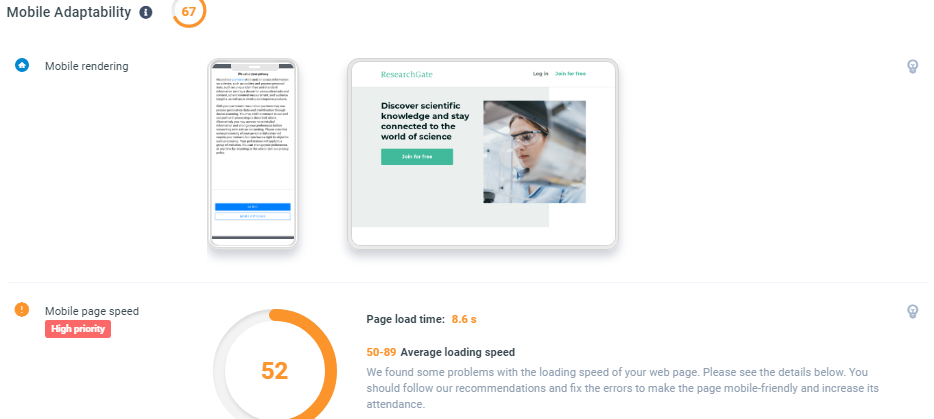
Mobile adaptability details how well your page loads its mobile version. This section delves heavily into performance, which is the next section. Below is a list of items necessary to this analysis:
- Mobile page speed: how fast the mobile version of your website loads. You can address this issue by avoiding clunky or unnecessary chunks of code and ensuring text is visible as soon as possible.
- AMP check: This checks to see if your mobile page supports AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages). AMP is Google's answer to providing quick loading webpages.
- Viewport / Content width / Font size - This section checks to ensure that all of your content is displaying correctly on mobile devices.
- Tap elements - Ensures that mobile devices can easily tap anything that desktops would click (navigation elements, CTA buttons, etc.).
Section Six: Performance
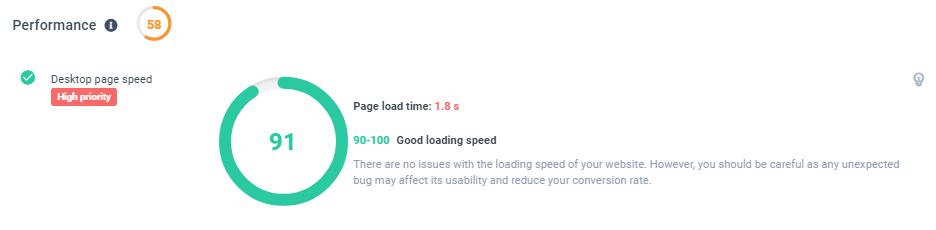
Performance deals in the page load speed of your site on a desktop. It holds many similarities with the mobile adaptability section:
- Desktop page speed: The speed at which it takes your page to load.
- Server response time: The speed at which your server responds to your request to visit the website.
- Asset modification/compression: Ensuring that images or videos available on the page are compressed and loaded so they can load quickly.
- Asset cacheability: Allowance of assets to be cached on your site visitors' computer, so they already have portions of your website at easy access.
All Other Tools For Website Analysis
The remaining sections of this website delve into the importance of having a social media presence, website security, and domain information. We recommend you check out this section for your input. Still, it boils down to the importance of being on social media and investing in security (SSL certificates) for your website. For further details on this, we recommend you contact Semalt's team of specialists.
Final Thoughts
When everything is said and done, Semalt's audit count comes to 54 different data points that you can apply to your SEO tools. It also provides you with reminders regarding security, social media, and page speed. All of which combine to give Google a trustworthy website to review.
If you need help creating your website that Google can find, we suggest checking out Semalt's website analyzer to see how you can improve.